A medical implant is a man-made device used to replace, support or enhance the functions of biological structure of the body. In strong contrast a transplant is a biomedical tissue.
Various categories of implants are
Surface implants: The implants that contact the body surface and are made up of biomedical material like titanium, silicone or apatite (used as required)
Electro-medical Implants: Now dayâs implants incorporate electronics and are powered by a battery like artificial pacemakers and cochlear implants.
Bioactive implants: Medicinal implants that also deliver medicine like medicated stents or subcutaneous drug delivery systems.
Applications of medical implants: The most common medical implants are the pins, rods, plates and screws that are used in orthopedics for fractured bones. Dental implants are also common today.
Need for change
More and more of the medical implants are now electricity powered like the very commonly needed battery powered artificial pacemaker and cochlear implant. Continuous uninterrupted power supply is the most elementary challenge. The challenge is to keep the pacemaker working round the clock without interruption. The limited power source of the battery is a challenge that need frequent replacements. With the advancement in technology the devices are becoming smaller day by day and the power consumption is thus reducing. The efforts are focused on using the human body as the source of the little power that these devices require so that these implants can work virtually perpetual, and need minimum maintenance or replacement. This will not only avoid repeated surgeries but will also improve the quality of life and the cost involved in repeated surgeries could also be reduced.
Research is on with the stretchable nanogenerators (made of piezoelectric material, used for converting kinetic energy into electrical energy) that can use the lung motion to power medical implant.
What’s Next?
To complete the portability factor of any device the most important issue is the continuous uninterrupted power supply and if we can device a method where we can use our body to provide the little amount of energy to run these implants then the implants will never need external source of energy. The next level implants are the implants that are self powered.
1. Heart-powered pacemaker
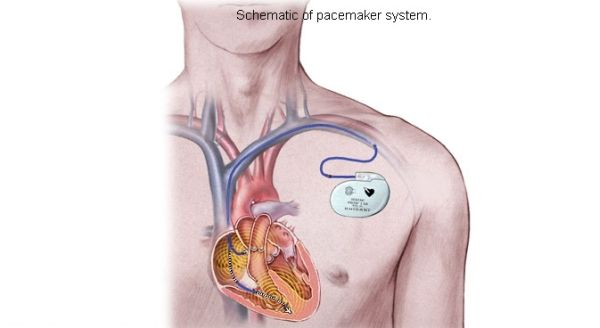
What’s new?
Ever seen a self-winding wrist watch? Just as you walk the kinetic energy of your moving arms is stored as potential energy in the springs inside the watch to give watch energy to tick. In the same fashion scientists have designed pacemakers that are powered by the motion of the patients own heart. The scientists at the Stanford University have made a device that can use heart motion to provide energy to the pacemaker. The power generated is more than that required by the pacemaker and can be stored in the battery for emergency or future use. Currently the battery life of the existing battery operated pacemakers is theoretically 10 years, but practically last 4 to 5 years.
What difference will it make?
By the use of heart powered pacemaker the life of the pacemaker can be increased. The stretchable piezoelectric material made of certain types of crystals and ceramics when distorted produce a small electric current which can power the pacemaker implant. Electromagnetic induction by the heart motion can also be used to generate small electric energy to power the pacemaker. Although the power generated is quite small and seems impractical to power currently available pacemakers, but with the help of nanotechnology the pacemakers are also becoming miniature in size and require much less power (sufficient enough that is generated by piezoelectric material) that makes the future of heart powered pacemakers practical.
Problems
One of the main problems associated with all the implants is the risk of getting infected or rejected. The challenge is to make a device that is accepted by the body and can prevent any sort of infection too.
2. Photovoltaic eye implants
What’s new?
Retinopathy is the condition where the photoreceptor cells of the retina gets damaged. These cells are responsible for converting the image focused on it to electrical impulses that are sent to the brain to generate an image. Photovoltaic retinal implants are used to replace the damaged retinal photoreceptors so that the image formed could be converted to electrical impulses interpreted by the brain.
What difference will it make?
The patients who are blind may be by birth or due to some accident where they have damaged their retina which cannot be restored. Such patients will be able to see with the help of photovoltaic retinal implants. Once the photovoltaic retinal implant will become self powered the patients will not have to carry power source with them and can live free without hasltes.
Problems
The scientists faced two basic problems. One was to provide power to the implant and other was to provide data make the person see (image) to the implant. Both the problems are solved by using a camera on the specs from where the data (image) goes to a miniature PC inside the patientâs pocket from where the power and data (image) reaches the photovoltaic retinal implant.
3. Serial In-vivo Transducer (SIT)
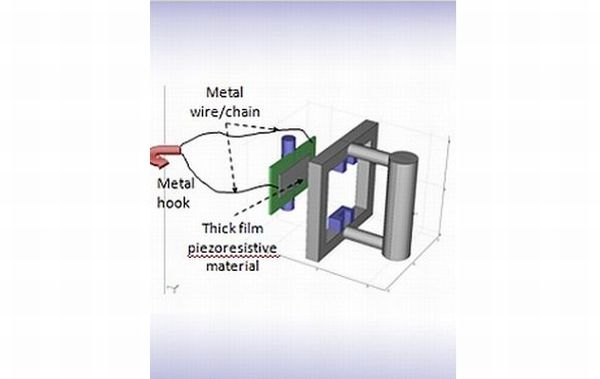
What’s new?
Serial In-vivo Transducer (SIT) is a newly designed self-powered sensor developed by a researcher from the University of Southampton. This implant helps to monitor progress of the knee surgery. This implant is particularly very useful in measuring the very sensitive tendon force during Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) reconstruction during surgical procedure. ACL is seen to be the most commonly injured ligaments by the athletes. This research recently came to limelight when ACL ligament of Tiger Woods got injured and this implant used for his knee surgery. Piezoelectric material that generated power by knee movement can power the SIT sensor that can continuously monitor the condition of the ACL.
What difference will it make?
This is a very useful implant that keeps a check on the most important ligament of the athletes. This device is in the phase of infancy and can be applied to various other areas like prosthetic hands.
Problems
Since this technology is in the initial phase the device may have compatibility issues with the body and its various applications are still under research.



