When we think about renewable energy, we usually talk about solar energy. Nevertheless, apart from solar energy, there are other significant renewable sources of energy too. Amongst them, wind energy might be the most prominent. In fact, generating energy using a wind turbine is a very common practice. Gigantic rotating wind turbines is a common sight in many parts of the world. In addition, unlike solar energy wind energy is available throughout the day. Therefore, it has much better potential to work practically as clean energy. However, wind energy too has its own pros and cons, which become even more evident when we consider two ways of utilizing it i.e through Vertical Axis Wind Turbines and Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines.
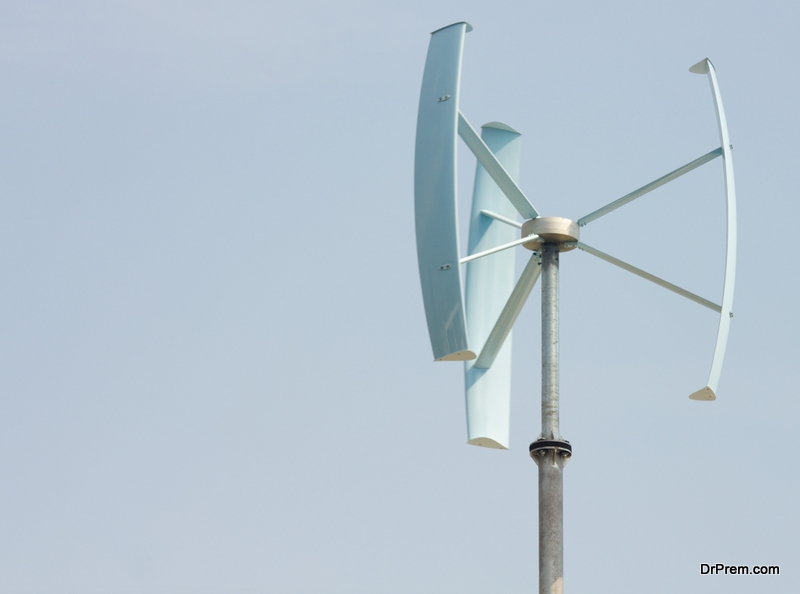
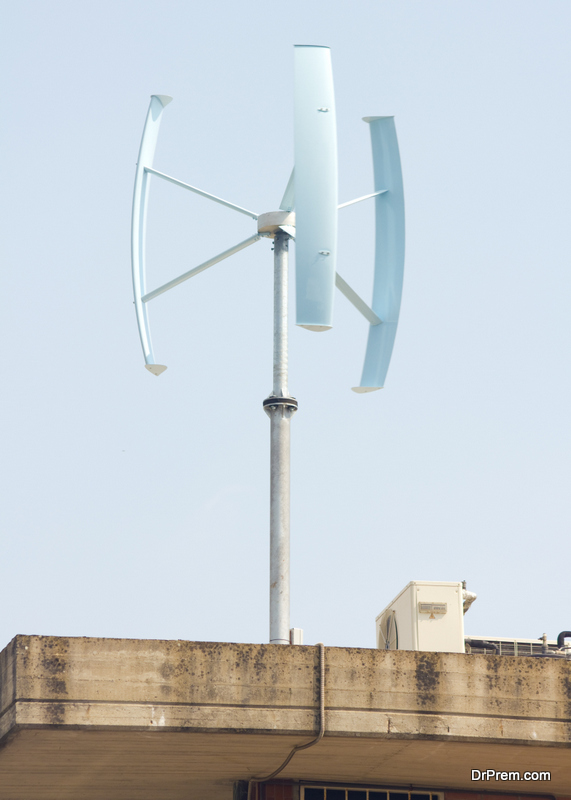
One of the most significant developments in the last few decades is a spurt in innovations for the production of energy from renewable sources. The vertical axis wind turbine ( VAWT) is a recent example of this trend. Technologically, the VAWT provides some advantage over the traditionally used horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT). Furthermore, a new researcher has shown that it can produce more energy even when the speed of the wind is low and less area is available for the wind power plant. This is so because the rotor shaft of the VAWT. It is vertical and works even when the turbine does not point towards the wind.
However, there are some disadvantages as well. Here we will analyze all the issues related to VAWT in detail.
The good
Greater efficiency
 Research has shown that VAWT could increase the efficiency of the wind farm by almost six to nine times as compared to the HAWT. The use of VAWT also decreases the total demand for land for the wind farm. It is because one can place them close to each other. This is possible as they do not require the erection of huge towers for mounting the turbines.
Research has shown that VAWT could increase the efficiency of the wind farm by almost six to nine times as compared to the HAWT. The use of VAWT also decreases the total demand for land for the wind farm. It is because one can place them close to each other. This is possible as they do not require the erection of huge towers for mounting the turbines.
One can mount the VAWT closer to the ground, even at the height of 10-meters. Moreover, even the turbine generator and the gearbox have their place lower on the ground. This reduces the maintenance cost. Moreover, it is also less harmful to the birds. In addition, it provides no interruptions to the radar systems and airplanes. One can also use it at sites where wind directions vary rapidly.
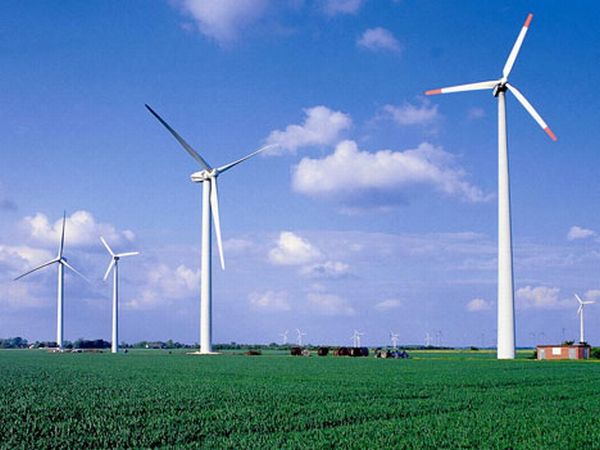
In comparison, traditional HAWT requires a large amount of land. It is because the wind turbines are there at a distance to avoid the intersections of the wakes of adjacent turbines. In present times, people generally utilize taller wind turbines. These are erected for accessing wind with greater speed to overcome this aerodynamic constraint. But still, it costs much more and has visual, radar and acoustic and environmental impacts.
Can this be better?
Despite certain advantages, it has been said that the VAWT do not match the scale of the HAWT. Researchers would have to find the solutions of following limitations of the VAWT for making it a better option for wind power generation and wider applicability.
Some more advantages
In a vertical axis wind turbine, the generator and the gearbox are mounted towards the base. Therefore, the maintenance cost of the generator and the gearbox is comparatively less as compared to the conventional wind turbine where they are located at the top of the shaft.
Since in the vertical axis wind turbine the blades are wrapped around the shaft, they are normally safer for birds. In a horizontal axis wind turbine, the blades spin in the air causing all sorts of problems for birds.
Unlike horizontal axis wind turbines, whose position strategically ensures that wind strikes the blades at the right angle, vertical axis wind turbines can make use of wind from any and all directions to generate electricity. This adds to their efficiency. Furthermore, it also allows the users to install them in areas with variable wind direction.
People living in the neighborhood of a conventional horizontal axis wind turbine often complain of the constant noise and vibration that their spinning blades produce. To the contrary, vertical axis wind turbines operate a lot more silently and do not cause any vibrations to trouble people living in their close proximity. This silent and vibration-free operation makes vertical axis wind turbines a better option for placement in urban areas.
The bad
Less efficient than those produced by horizontal axis wind turbines
The energy-producing capacity of the existing designs of VAWTs is much less as compared to the HAWT. This is so because the height of the VAWT is less and it cannot reap the benefits of higher wind speed at greater altitudes. It cannot be mounted on high towers. Moreover, the VAWT requires some external energy for initiating the movement of the blades of turbine because it has very low starting torque. Also, it needs additional support in the form of wires for keeping the structure intact.
Can this be avoided?
Yes. A new research by John O. Dabiri of the California Institute of Technology this year has shown that many problems associated with the VAWTs could be overcome by the reconfiguration of turbine placement in the wind farms and with the use of new counter-rotating VAWTs.
They would also minimize many challenges associated with the establishment of large HAWTs, such as the cost and logistics of manufacture, installation and transportation. Also, massive structures for holding the turbine on top could be built. It will also reduce the downward thrust experienced by the wired structure.
The ugly
Mounted closer to the ground, less wind speed
As said above, the VAWT are mounted closer to the ground and receive less wind speed. Also, it has been found that the blades of VAWTs are prone to fatigue and sometimes the blades broke apart, thus stalling the entire process of power productions.
Why are we so critical?
The pace of development of technologies for the generation of electricity from wind has been very slow. It started in the 19th century in Denmark but till the 1970s only small wind turbines for charging purposes were available. Considering this along with the ever growing need of ‘green’ energy, we ought to be critical of all new innovations that promise some thing better than the past.
The Bottomline
If the new research is to be believed, the VAWTs could herald a new era of ‘flexible’ wind farms that could be used in areas, including your neighborhood, where wind farms have not been traditionally established. It would also boost the recent efforts put by many governments of the world for tapping the natural energy of wind. As, many large scale wind farms have been established in many cities of the world in recent times.