The state of the environment is no longer an issue to be taken lightly. Excessive global warming has led to dramatic climate change and erratic weather. There are many more instances of extreme weather leading to damage on land and in the seas, both personal and commercial. China and Japan have now launched satellites to monitor the environment, so that people and businesses can be warned in time of imminent storms and typhoons. Another reason is to monitor greenhouse gas emissions in order to curb/ reduce global warming.
Chinese and Japanese satellites to monitor environment
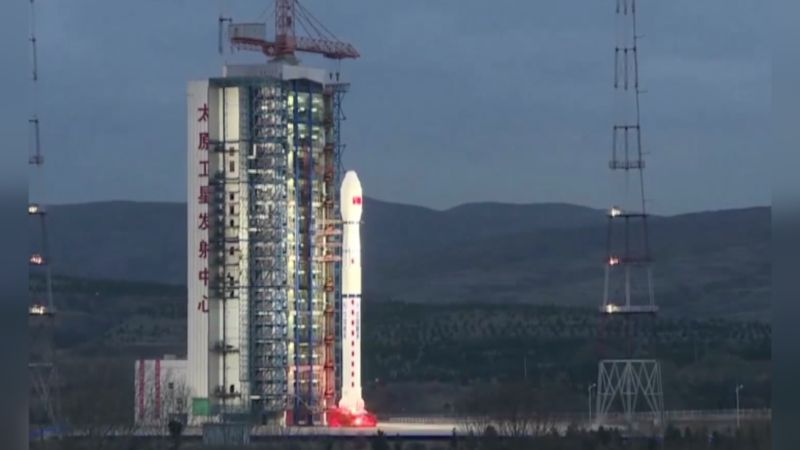
HY-2B carrying on from HY-2A
Image Source : video.cgtn.com
China recently sent its new satellite HY-2B which would take over from its predecessor HY-2A which functioned as an ocean dynamic sat. The satellite was launched using a March 4B rocket from Taiyuan Satellite Launch situated in the north of China’s Shanxi Province.
The HY-2B will be followed by the HY-2C as well as the HY-2D to observe the maritime environment. The greenhouse gas observing satellite HY-2B will be able to provide all-time and all-weather environment, and has been designed to last for 5 years in space. The incredible satellite will cover up to 90% of all the oceans in the world and obtain precious data regarding the temperature of the surface of the oceans/seas, sea ice, rainfall levels and wind speed.
This data can help in many ways to protect people from storms and many lives of fishermen can be saved. The environment too would benefit as satellites to monitor environment, such as this one, will observe marine environment and point out the areas which are most polluting, and the government and individual can take the necessary steps to stop atmospheric pollution.
Features of the HY-2B satellite
China’s first of the satellites to monitor environment, HY-2A stayed in orbit for seven years. Based on it, the HY-2B was made with some additional features. It has two new systems – one of them is used for space observation in order to track/monitor vessels with automatic identification system.
The other innovative feature is the ability and capacity to transmit, store, receive buoy measurement data in China’s offshore as well as other areas in the sea.
The Chinese government has announced the major role HY-2B will be playing in China’s environment management, disaster relief and ocean resource surveys. China has been bogged down by heavy pollution due to industrial and vehicular emissions. This satellite will empower China’s environmental cleaning efforts to bring down the pollutants to a less toxic level. The satellite network which are planned to follow HY-2B will strengthen the maritime policy of China.
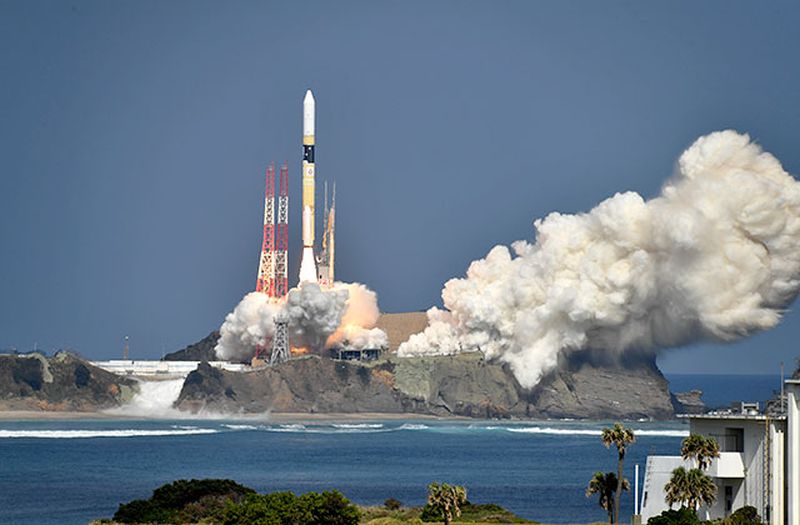
Japan launches Ibuki-2 (GOSAT-2) green satellite
Image Source : global.jaxa.jp
One of the satellites to monitor environment, the Ibuki-2 (GOSAT-2) was launched from the Tanegashima Space Center. The satellite has been touted as Japan’s most accurate sat greenhouse gas observing satellite. The satellite was developed in collaboration with Japan’s Environment Ministry, Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency and Japan’s National Institute for Environmental Studies and cost around 44 billion yen.
From its height of 600 kms above the earth, the sat will be able to detect the minutest concentration changes of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide. The satellite is so sensitive that it can sense the presence of CO2 and other gases in about 200 liters of fluid i.e. if a few drops of lotion are inserted in about a bathtub of water. This would enable Japan to monitor emissions and bring them down to acceptable levels.
Khalifasat, Diwata 2 launched from Japan
Space observation of dangerous gases in the atmosphere of the earth will now be done by a few countries apart from China and Japan. The Khalifasat which has the additional distinction of being the first satellite developed completely by the UAE, is a remote sensing sat. It was made at the Mohammed bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) located in Dubai.
The Khalifasat, one of the satellites to monitor environment, will be operating from a height of 613 kms above earth and can last in space for 5 years. The satellite which weighs 330 kg is fitted with a high res pushbroom multispectral imager, which has 2.98m in 4 multi-spectral bands for infrared imaging. It also has a 0.7m to detect panchromatic imagery. The imagery from the Khalifasat will be used for disaster relief, including the detection of oil spills, urban planning, changes in the environment and other uses for all UAE governmental entities and UAE entities. The images could be used for commercial purposes later.
Diwata 2
Image Source : flyingketchup.ph
This is the second of the satellites to monitor environment developed by the Philippines’ DOST (Department of Science and Technology), Tohoku University and Hokkaido University, Japan. The satellite weighs only 56 kg and has a lifespan for 5 years. Diwata-2 is fitted with an SMI (Space borne Multispectral Imager), amateur payload, as well as HPT (High Precision Telescope).
Philippines is a country which has faced many natural disasters in the past. With the data sent by the satellite, the country will be able to observe marine environment and better prepared to face natural calamities in the future and put in motion effective disaster relief measures. The government has also planned to use the information from Diwata-2 to assess post-disaster damage to life and property as well.
Smaller satellites were also sent by Japanese universities
The Japanese rocket launched two small sats Ten-Koh and AUTcube 2 as well for environmental monitoring.
Ten-Koh
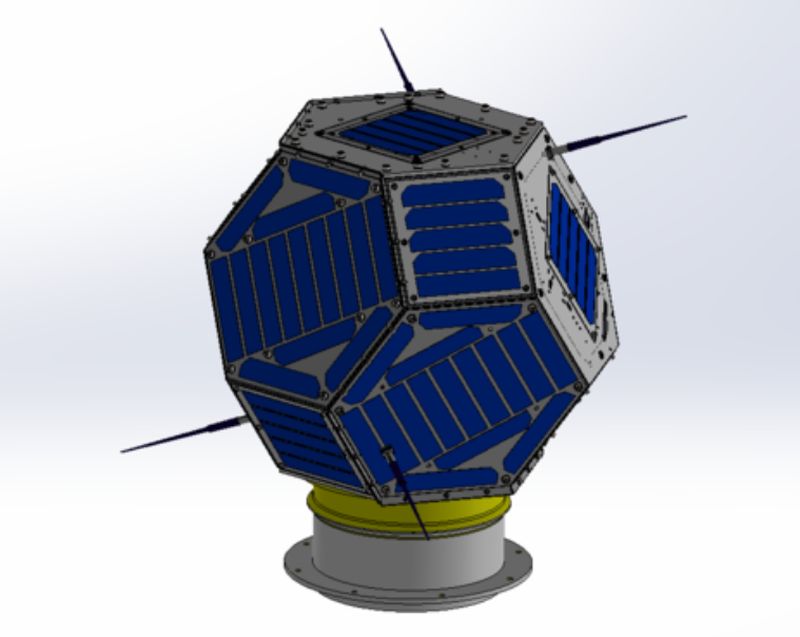 Image Source : kit-okuyama-lab.com
Image Source : kit-okuyama-lab.com
The tiny satellite weighs only 45 kg and was developed by the Kyushu Institute of Technology. The design of the satellite is quite innovative, as it is spherical in shape and covered all over with unique solar cells. The function of the satellites will be to measure/monitor the degradation of the materials due to radiation and magnetic flux in LEO environment.
AUTcube 2
The cubesat was made by the Aichi University of Technology with the specific mission – to demonstrate VR (Virtual Reality) as well as satellite communication via LED bulbs. The cubesat also carries an extremely tiny telescope to measure astronomical observations.
The Japanese satellite GOSAT-2 will be performing an important function for the benefit of the entire world, as it will monitor how well countries are fulfilling their promise to curb greenhouse gases according to the 2015 Paris Climate Change agreement. This can help to keep emissions at a low, which is very important if we are to ensure a better future for the planet.






