Global warming due to increase in atmospheric greenhouse gases has forced the global leaders to pledge funds for projects aimed at controlling global warming because it can cause severe danger to earth. Some governments are investing millions of dollars on developing satellites that can be used to monitor earth in order to study the change in climactic conditions due to global warming. Here is a list of 5 satellites that have been launched to monitor the impact of global warming on our planet.
1. Gravity Field and steady-state Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE)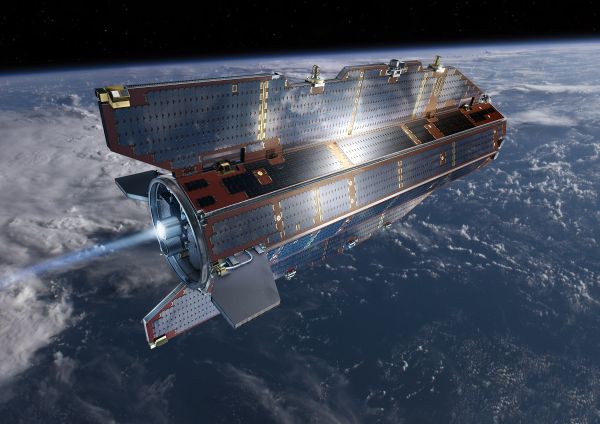
Launched in 2009 by ESA, GOCEâs main function is to collect detailed information on matters related to the gravity of earth. The satellite which is currently in space is five meters long and it is the first part of its âEarth Explorerâ program. The weight of this satellite is 1,050kg. This satellite is capable of observing and catching slightest change in the gravitational field of earth very accurately because it is positioned just 260 kilometers above the earth. This satellite is working well so far, sending raw data to the earth. This data has been analyzed deeply by the scientists to gauge the impact of global warming on sea levels, circulation of ocean systems and the ice sheets. The main objective of the mission is to determine the anomalies of gravity field with an accuracy of 10â5 msâ2. This satellite was launched with a rocket vehicle from northern Russiaâs Plesetsk Cosmodrome.
2. TRMM satellite: Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission
Launched in November 1997, the main objective of TRMM is to show the transfer of heat and water vapors between the atmosphere and ocean. Worldâs premier space agency NASA is monitoring this project which was launched to measure earthâs tropics and subtropics precipitation. The data provided by TRMM is used for climate models and is also used to improve these models. TRMM is loaded with instruments, out of which The Precipitation Radar is the most important one. The other two instruments are TRMM Microwave Imager (TMI) and Visible and Infrared Scanner (VIRS). Built by Japan-based National Space Development Agency (NASDA), The Precipitation Radar is first space borne instrument, which is capable of providing 3D maps of the storm structure. NASA claims that this radar provides interesting and useful information on the rainâs intensity and distribution. It also provides information about the rain type and the depth of storm. This satellite is a part of the Mission to Planet Earth project launched by NASA.
3. Formosat3 / COSMIC (F3C)
This was launched on 15 April 2006 from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. This mission is jointly run by US and Taiwan. The mission is to study the change in the weather and climate of earth as well as space weather. This mission also takes care of geodetic research. As part of mission, six identical micro satellites were positioned in the orbit at 500 km away from earth. The satellites are carrying GPS radio occultation receiver, a Tri Band Beacon (TBB) and a Tiny Ionospheric Photometer (TIP).
The launch vehicle of this satellite was Minotaur and this mission will last for 5 years. After its launch, the micro satellites took more than a year to move into the correct positions. Once they moved into the desired position, these satellites started providing useful information.
4. CloudSat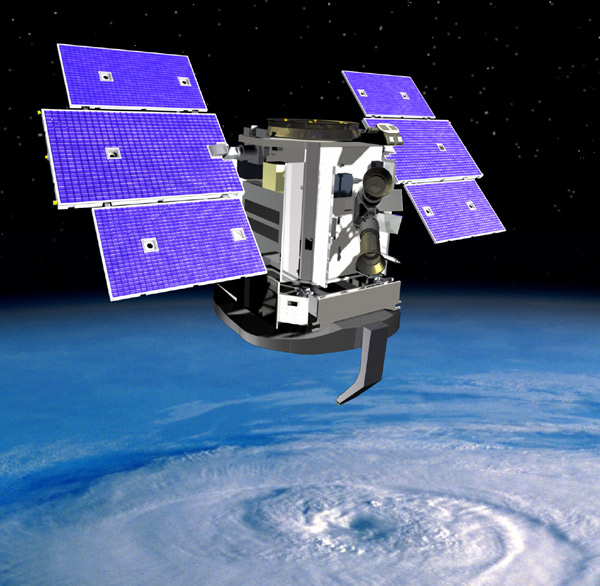
Launched on April 28, 2006 on a Delta II rocket, the CloudSat is a part of NASAâs space mission and it is an earth observation satellite. The most important component of this satellite is a 94-GHz Cloud Profiling Radar (CPR). This radar is capable of measuring the power back-scattered by clouds. This radar was developed at Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) of NASA. The JPL is located in Pasadena, California. Canadian Space Agency has supplied the hardware contributions. The CPR measures the properties of cloud and their altitude and it helps the scientists to know more about the questions related to global warming by providing information about relationship between climate and clouds.
5. CALIPSO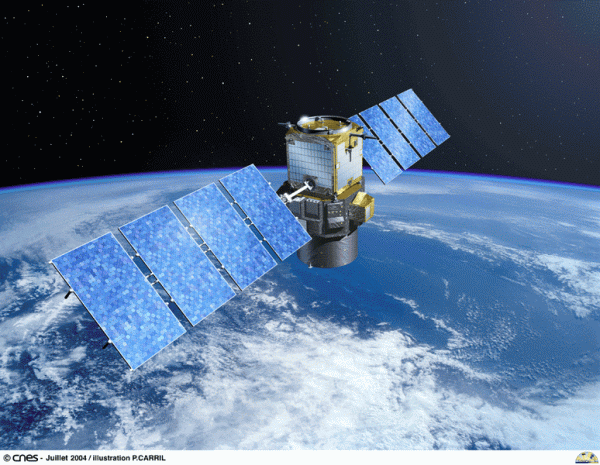
Built in the Cannes Mandelieu Space Center, this environmental satellite has been designed and developed jointly by NASA and CNES in France. Launched on April 28, 2006, on a Delta II rocket, the Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) carries passive and active sensing instruments, which are used for round-the-clock monitoring of aerosols and clouds. CALIPSO orbits near Aqua and Cloudsat in âA Trainâ constellation. This satellite helps the scientists in understanding the climatic systems and the changes in them due to global warming.




